In modern society, bridges serve as important transportation hubs connecting cities and regions, and their safety is crucial. However, the structure of bridges is complex and subject to various natural and human factors, facing varying degrees of safety risks. Therefore, bridge safety monitoring technology has emerged, which is not only an important means to ensure bridge safety, but also an intangible barrier to safeguard pedestrian and vehicle safety.
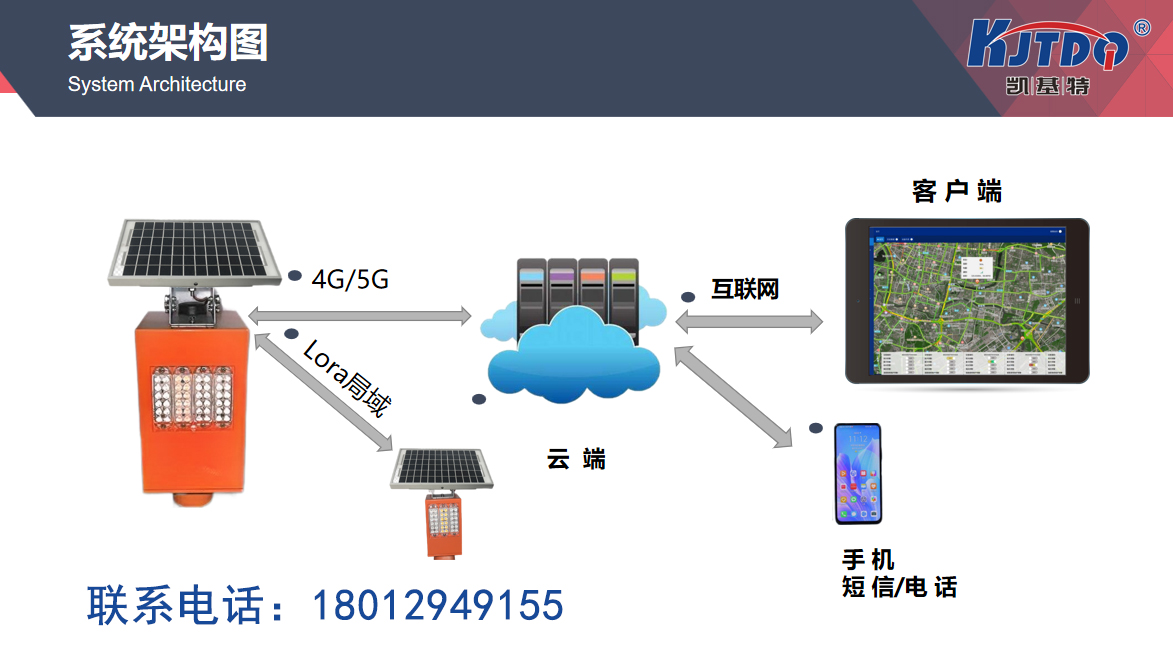
Bridge safety monitoring technology is a technology that uses high-tech means to monitor the real-time health status of bridge structures. It can accurately detect subtle changes in bridges, such as cracks, displacement, tilt, etc., and issue timely alerts in the early stages of problems. The core of this technology lies in the use of various sensors, data acquisition devices, and analysis systems to monitor and analyze various parameters of bridges in real time, providing scientific basis for bridge maintenance and repair.
With the advancement of technology, bridge safety monitoring technology has developed rapidly. The current monitoring system can not only monitor the static structure of bridges, but also capture dynamic changes in real time. For example, when a bridge is impacted by vehicles or natural disasters, the monitoring system can immediately detect abnormalities and respond quickly. This precise bridge safety monitoring technology greatly improves the safety factor of bridges and reduces the incidence of accidents.
In addition, bridge safety monitoring technology also has strong preventive functions. Through long-term monitoring of bridge structures, the system can accumulate a large amount of data, analyze the health status of the bridge, and predict potential risks. This data-driven bridge safety monitoring technology can not only help engineers detect problems in a timely manner, but also provide valuable references for future bridge design and construction.
The application scope of bridge safety monitoring technology is very wide, whether it is large urban bridges, cross river bridges, or small bridges in rural areas, they can all benefit from this technology. For example, in big cities, bridges have high traffic flow, complex structures, and high safety risks. Through bridge safety monitoring technology, these bridges can be monitored 24 hours a day to ensure their stability under high loads. In areas with frequent natural disasters, such as earthquake and flood prone areas, bridge safety monitoring technology is indispensable. It can detect the damage of bridges in the first time when disasters occur, providing important basis for rescue work.
However, despite the many advantages of bridge safety monitoring technology, it also faces some challenges. Firstly, the technology cost is relatively high, especially for small and medium-sized bridges, and the comprehensive deployment of this technology may increase financial pressure. Secondly, the complexity of technology requires professionals to operate and maintain it, which may lead to a shortage of technical talent for some underdeveloped areas. Finally, although bridge safety monitoring technology can provide early warning and monitoring, how to take effective repair measures in a timely manner after discovering problems is also a problem that needs to be solved.
However, the role of bridge safety monitoring technology in ensuring bridge safety is irreplaceable. With the continuous advancement of technology, the cost of future bridge safety monitoring technology is expected to decrease, and its functions will also become more intelligent and automated. For example, the introduction of artificial intelligence can enable monitoring systems to have autonomous learning and judgment capabilities, thereby further improving the accuracy and efficiency of monitoring.
In the long run, bridge safety monitoring technology is not only a technological innovation, but also a manifestation of social responsibility. It has ensured the safety of countless pedestrians through technological means, providing a solid foundation for economic development and social stability. Whether it is the government, enterprises, or research institutions, they should attach importance to the development and application of this technology, and promote its role in a wider range of fields.
Overall, bridge safety monitoring technology has become an indispensable part of modern bridge engineering. It provides strong guarantees for the safe operation of bridges, reduces safety accidents caused by bridge structural problems, and greatly improves people's travel safety. In the future, with the further development and improvement of technology, bridge safety monitoring technology will play a greater role and contribute more to the sustainable development of society.
As a high-tech means, bridge safety monitoring technology is not only a standard configuration in modern engineering, but also an emphasis and respect for life safety. Its promotion and application will bring people more sense of security and happiness. The continuous development of this technology will also drive the entire industry towards a more intelligent and efficient future. Bridge safety monitoring technology is undoubtedly an indispensable guardian in our modern life.
1. How does bridge safety monitoring technology work?
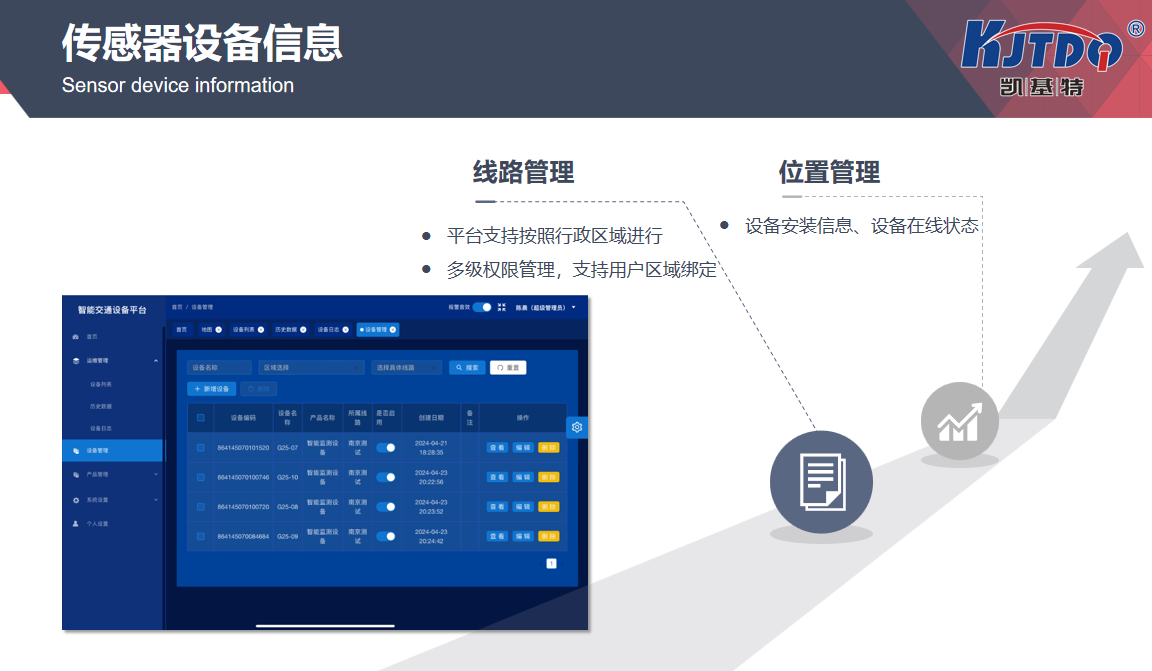
Bridge safety monitoring technology relies on the collaborative operation of various high-tech equipment and systems. Typically, these systems include sensors, data acquisition devices, analysis software, and remote monitoring platforms. Sensors are installed in key parts of bridges, such as bridge piers, main beams, and connection points, which can detect changes in the structure in real time, such as vibration, displacement, stress, temperature, etc. These data are transmitted to the central system through data collection devices, and the system will analyze them based on preset thresholds. If abnormal conditions are detected, such as crack propagation or structural deformation, the system will immediately issue an alarm to notify the maintenance team to take action.
At the same time, bridge safety monitoring technology also combines big data analysis and artificial intelligence technology to conduct trend analysis and predict potential risks through long-term accumulated data. This predictive function is particularly important because it can take preventive measures in advance before problems occur, avoiding more serious accidents. In addition, the monitoring system can be integrated with the traffic management system to automatically adjust traffic flow when necessary, further improving the safety of the bridge.
2. What are the application scope of bridge safety monitoring technology?
The application scope of bridge safety monitoring technology is very wide, covering various types and scales of bridges. Firstly, there are large urban bridges that usually carry a large amount of traffic flow, have complex structures, and face high safety risks. Through bridge safety monitoring technology, the health status of the bridge can be monitored 24/7 to ensure its stability under high loads. Next is the cross river bridge, which usually spans wide waters and is greatly affected by natural factors such as wind and waves. The monitoring system can capture the impact of these external environments on the bridge structure in real time and promptly warn of potential safety hazards.
In areas prone to natural disasters such as earthquakes, floods, and mudslides, bridge safety monitoring technology is particularly important. By continuously monitoring the bridge structure, the system can quickly assess the damage to the bridge during disasters, guide emergency rescue and bridge repair work. Even small bridges in rural areas can obtain basic safety data through simplified monitoring technology to prevent the occurrence of sudden accidents.
3. What are the advantages and challenges of using bridge safety monitoring technology?
Bridge safety monitoring technology has significant advantages, firstly in improving the safety of bridges. Through real-time monitoring and warning systems, maintenance teams can identify and resolve issues in the early stages, thereby avoiding potential catastrophic consequences. Another advantage of this technology is that it extends the service life of the bridge. Through long-term monitoring, the health status of the bridge can be continuously tracked, and maintenance work is more precise, avoiding excessive repairs and unnecessary resource waste.
However, bridge safety monitoring technology also faces some challenges. Firstly, there is a cost issue, especially for small and medium-sized bridges, the comprehensive deployment of this technology may increase construction and maintenance costs. Secondly, there is technical complexity, as bridge monitoring systems require professional personnel to operate and maintain, and in some underdeveloped areas, such talent resources may be relatively scarce. Finally, although monitoring technology can detect problems in a timely manner, how to quickly and effectively repair them remains a challenge, especially when dealing with complex structural damage.
4. How to integrate bridge safety monitoring technology with other technologies?
The integrated application of bridge safety monitoring technology and other related technologies can further enhance the overall safety level of bridges. For example, the monitoring system can be integrated with the intelligent traffic management system. When there is an abnormality on the bridge, the system can automatically adjust traffic signals, restrict or divert traffic, in order to reduce the load on the bridge. This integration not only enhances the ability to respond to emergencies, but also optimizes traffic flow, reduces congestion and accidents.
In addition, bridge safety monitoring technology can also be combined with drone monitoring technology. Drones can carry high-resolution cameras and other sensors to conduct comprehensive external inspections of bridges, capturing subtle cracks or structural damage that are difficult for the human eye to detect. By integrating data with ground monitoring systems, maintenance teams can more accurately locate problems and develop targeted repair plans. This technology integration not only improves the comprehensiveness and accuracy of monitoring, but also greatly reduces the cost and risk of manual inspection.