When we drive on bridges, it is often difficult to realize that these massive structures connecting the two sides and carrying countless vehicles and pedestrians need to be kept safe and stable at all times. However, with the passage of time, erosion from natural factors, and an increase in traffic load, bridges face various risks. How to ensure the long-term safety of bridges and how to detect and prevent potential structural problems in the early stages is the mission of the intelligent monitoring system for bridge safety.
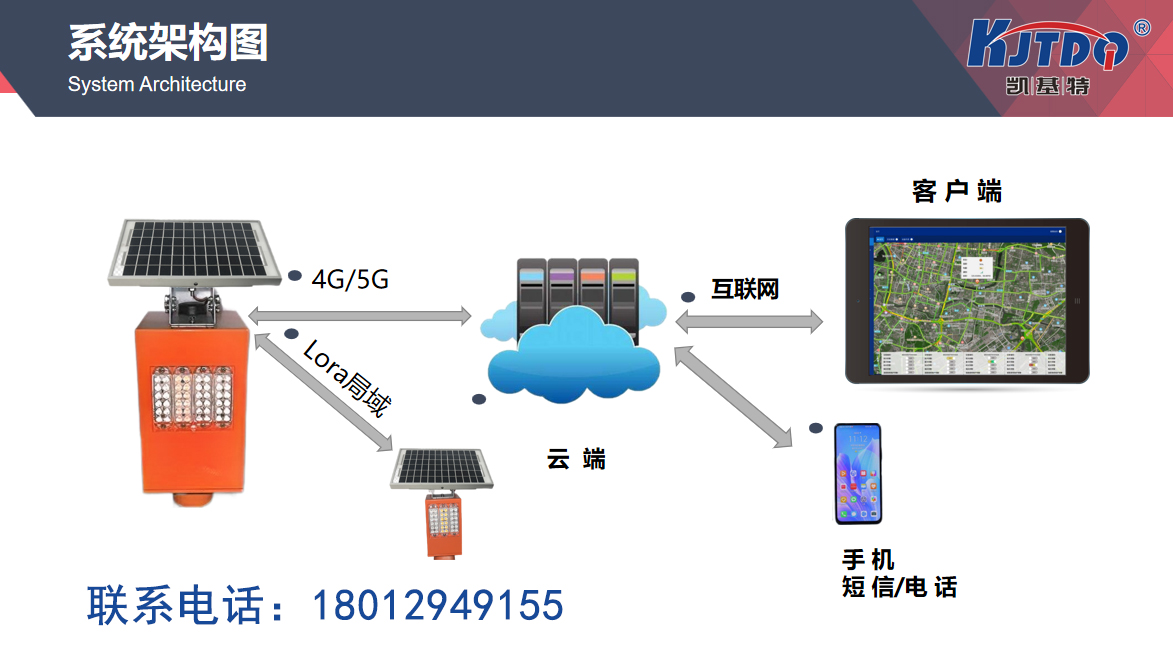
The intelligent monitoring system for bridge safety, in simple terms, is a real-time monitoring system that uses various advanced sensors, data acquisition devices, and intelligent analysis technologies to monitor the health status of bridges 24/7 and in all directions. These devices can accurately detect various indicators such as stress, deformation, temperature, and humidity of bridges, and summarize these data into a central monitoring system for analysis. If any abnormal situation is found, the system will immediately issue an alarm to remind relevant departments to conduct further inspection and maintenance.
Why is intelligent monitoring of bridge safety so important? Let's think about how crucial the role of bridges is in urban transportation networks. Once there is a problem with the bridge, it will not only cause traffic interruption, but may also bring huge casualties and economic losses. Therefore, the safety of bridges must not be taken lightly. Traditional bridge inspections often rely on regular manual inspections. Although this method is essential, it also has limitations, such as longer inspection cycles, limited detection accuracy, and constraints on human resources. The intelligent monitoring system for bridge safety can make up for these shortcomings and achieve real-time control of the bridge status.
In the intelligent monitoring of bridge safety, sensor technology is undoubtedly the core. Different types of sensors can monitor different parameters of bridges. For example, acceleration sensors can monitor the vibration of bridges, displacement sensors can detect the deformation amplitude of bridges, and temperature and humidity sensors are used to evaluate the impact of environmental factors on bridge structures. These sensors are installed at critical locations on the bridge, forming a comprehensive monitoring network to ensure that any subtle changes are not overlooked.
Real time data collection and analysis is another important part of the intelligent monitoring system for bridge safety. The data collected by sensors will be instantly transmitted to the central processing system, which determines the current status of the bridge through comparison of historical data and analysis of algorithm models. If a certain indicator exceeds the safety threshold, the system will automatically sound an alarm and can further retrieve relevant data for in-depth analysis, helping engineers quickly locate the root cause of the problem.
The intelligent monitoring system for bridge safety not only performs well in responding to sudden problems, but also provides scientific basis for bridge maintenance and management through long-term data accumulation. By analyzing years of monitoring data, management departments can better grasp the aging trend and potential risks of bridges, thereby developing more reasonable maintenance plans, extending the service life of bridges, and reducing the frequency of major repairs or replacements. This not only saves maintenance costs, but also ensures the continuity and safety of transportation.
In addition to these obvious functions, the intelligent monitoring system for bridge safety also has more potential advantages. For example, with the development of IoT technology, more and more bridge monitoring systems can achieve remote control and intelligent management. Engineers can view the real-time operation status of bridges in the office, and even operate and debug them through mobile phones or tablets. This convenience greatly improves the efficiency of monitoring and maintenance, making bridge management more intelligent and modern.
Of course, the implementation of the intelligent monitoring system for bridge safety is not achieved overnight, as it requires high initial investment and subsequent maintenance costs. However, in the long run, this investment is very worthwhile. Considering the enormous risks and losses caused by bridge accidents, investing in bridge safety monitoring is undoubtedly a guarantee for future safety. This strategy of "preventing accidents before they happen" can greatly reduce the probability of bridge accidents and provide a solid foundation for the sustainable development of society and economy.
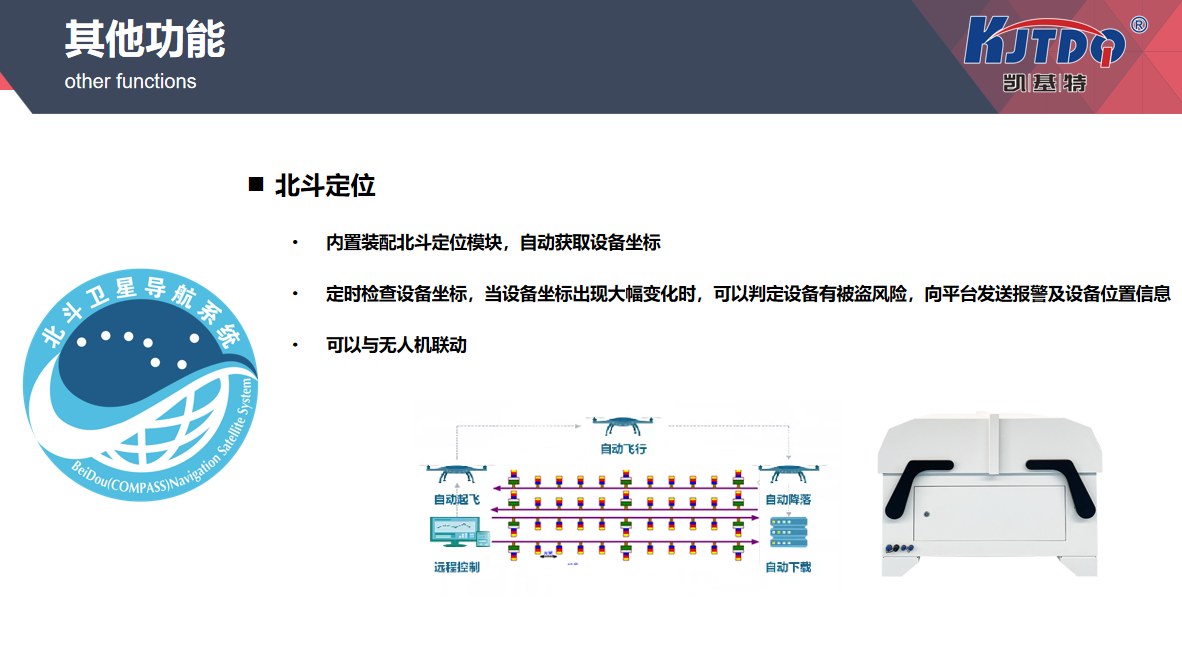
In conclusion, I would like to express a viewpoint: with the continuous advancement of technology and the increasing demand for infrastructure safety in society, intelligent monitoring systems for bridge safety will become increasingly popular and become a "standard" for every important bridge. In the future, we not only hope to see more bridges operating safely under such system protection, but also hope to create a safer and more intelligent transportation environment for us through the power of technology. Bridges are important links connecting people and cities, and intelligent monitoring systems for bridge safety are important tools for safeguarding these links. Only when every bridge is fully protected can we truly travel with peace of mind.
1. How can the intelligent monitoring system for bridge safety help prevent bridge accidents?
The intelligent monitoring system for bridge safety can detect potential structural problems in the early stages of bridge problems by monitoring key parameters such as stress, vibration, displacement, and temperature in real-time around the clock. Once there is an abnormality in the monitoring data, the system will immediately issue an alarm and notify the relevant management department to conduct inspection and maintenance, so as to deal with the problem in a timely manner before it worsens and prevent accidents from happening. This preventive measure can effectively reduce the risk of bridge accidents and ensure the long-term safety of the bridge.
2. Will the installation of the intelligent monitoring system for bridge safety affect the normal use of the bridge?
The design of the intelligent monitoring system for bridge safety takes into account the normal operation of the bridge, so the installation of the system usually does not affect the use of the bridge. Sensors and other monitoring devices are typically installed in critical structural areas of bridges. These devices are small in size, lightweight, and do not impose additional loads on the bridge structure. The installation process is usually carried out without affecting traffic, ensuring the normal operation of the bridge and uninterrupted passage.
3. How does the system address the issue of data errors in bridge monitoring?
The accuracy of data is crucial in intelligent monitoring of bridge safety. For this reason, the system usually adopts a redundant design of multiple sensors, that is, installing multiple sensors in the same location to ensure the reliability of data. At the same time, the system will perform cross validation and calibration of data, using advanced algorithms to filter out possible errors and noise. In addition, the system will regularly perform equipment calibration and maintenance to ensure the accuracy of monitoring data. This multiple safeguard measure greatly reduces the possibility of data errors and ensures the reliability of monitoring results.
4. How can the intelligent monitoring system for bridge safety help extend the service life of bridges?
The intelligent monitoring system for bridge safety can provide detailed structural aging data and trend analysis by continuously monitoring and analyzing the health status of the bridge. These data help engineers and managers to timely understand the aging status of bridges, identify potential structural problems, and develop scientific maintenance and repair plans. By timely maintenance and repair, the accumulation and deterioration of structural problems have been avoided, the service life of the bridge has been extended, and the need for large-scale repairs and replacements has been reduced.